
Lesson 3: DeFi Explained
Crypto World - Intermediate Level
← Back to TopicsWhat is DeFi?
DeFi stands for Decentralized Finance. It refers to a new financial system built on public blockchains like Ethereum and BNB Chain that removes banks and intermediaries.
Think of it like: banking without a bank — powered by code and community.
Key Features of DeFi
- Open access: Anyone with internet can participate
- Non-custodial: You control your own assets
- Permissionless: No KYC or approval needed
- Composability: DeFi apps work together like money Legos
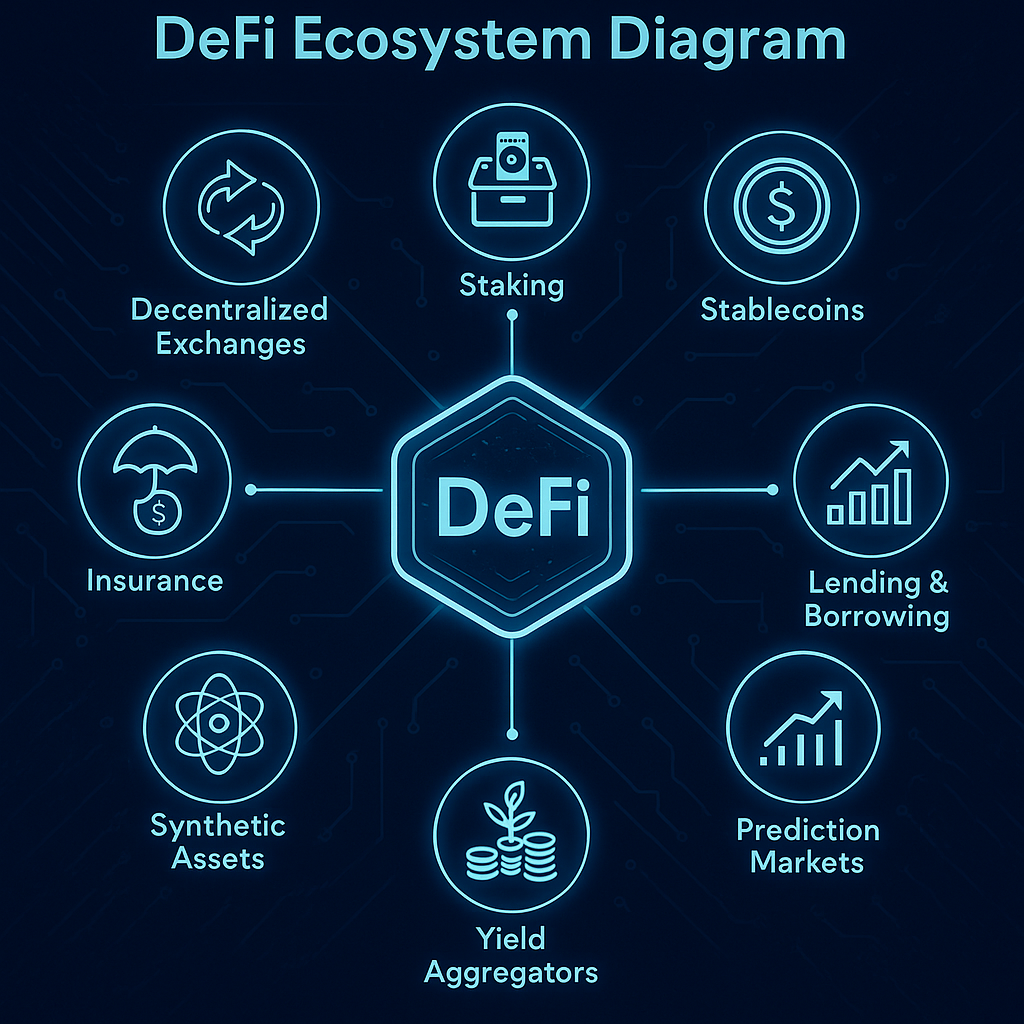
Popular DeFi Use Cases
- Lending & Borrowing: Platforms like Aave and Compound
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Like Uniswap or PancakeSwap
- Stablecoins: Such as DAI, USDC, BUSD
- Yield Farming & Liquidity Mining: Earn interest or tokens by providing liquidity
- Staking: Lock tokens to earn rewards and support network security
Benefits of DeFi
- Financial inclusion for the unbanked
- Transparency: all transactions are on-chain
- Global and 24/7 access
- Lower fees and faster settlements
Risks of DeFi
- Smart contract bugs or exploits
- Volatility in token prices
- Impermanent loss for liquidity providers
- Lack of regulation and protections
Next: We explore DAOs — decentralized organizations run by code and community.
Next Lesson →