
Lesson 1: Tokenomics & Utility Design
Crypto World - Advanced Level
← Back to TopicsWhat is Tokenomics?
Tokenomics refers to the economic design and mechanics behind a cryptocurrency token. It determines how a token is distributed, used, incentivized, and how it holds or increases in value over time.
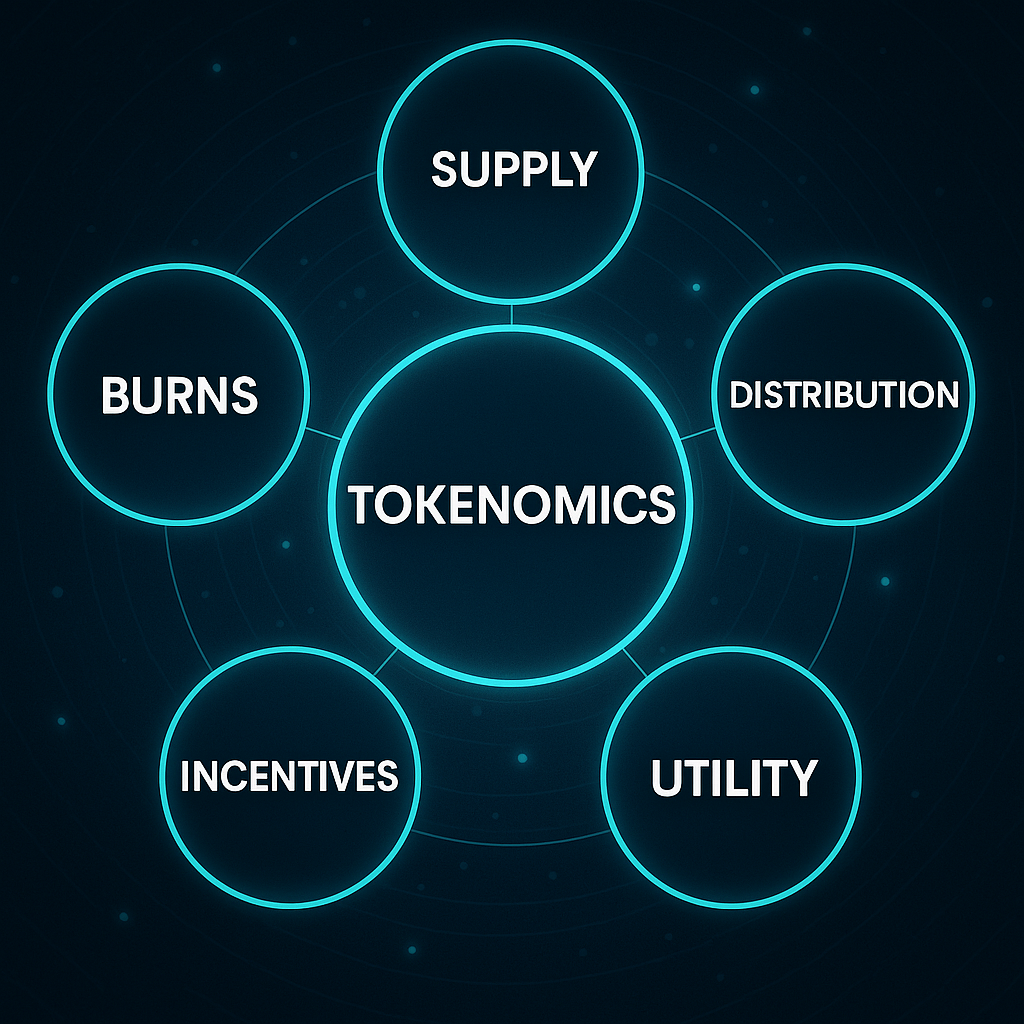
Key Elements of Tokenomics
- Total Supply: Fixed or inflationary supply of tokens
- Initial Distribution: Presale, airdrops, team allocation, staking rewards
- Incentive Model: Rewards for staking, participation, or referrals
- Burn Mechanism: Destroying tokens to reduce supply and increase scarcity
- Utility: What the token is used for (governance, payments, access, etc.)
Example: $FOFI Token charges an 8% fee per transaction. 4% goes to LP, 2% is reflected to holders, 1.5% to dev wallet, 0.5% to marketing — all part of its tokenomics.
Utility Design
A token with strong utility will be used regularly within the ecosystem. This gives it real-world value and demand. Examples of utilities include:
- Access to premium content or platforms
- Governance voting power
- Staking and rewards
- Discounts on services
- Fee payments or gas substitution
Token Types by Utility
- Governance Tokens: Used to vote on DAO proposals (e.g. UNI, COMP)
- Security Tokens: Represent assets and follow regulations
- Utility Tokens: Used inside apps and platforms (e.g. BNB, $FOFI)
- Stablecoins: Pegged to fiat or other assets (e.g. USDT, DAI)
Next: Discover how Layer 2 chains scale the blockchain while keeping it decentralized.
Next Lesson →